Position Paper: CenSES Energy demand projections towards 2050
10
energy system including all resources, energy production technologies, energy carriers, deman
gies and demand sectors. The model assumes perfect competition and perfect foresight and i
driven. Thus the projected energy demand has to be given exogenously to the model, and th
odel aims to supply energy services at minimum global cost by making equipment investments
operating, primary energy supply and energy trade decisions.
rway is developed by Institute for Energy Technology (IFE) on commission of The Norwegia
sources and Energy Directorate (NVE) and the development started in 2008. The time horizon o
l is from 2010 to 2050, with a flexibility of analysing years within this frame. TIMES-Norwa
l onshore energy use in Norway and the country is divided in five regions with exchange o
between adjacent regions and neighbouring countries.
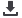
ture of the TIMES-Norway model is illustrated in Figure 5. The demand for various energ
energy price information and resource costs and availability are given exogenously to the model
ergy supply side, several conversion processes are represented in detail; e.g. electricity and hea
n. Transmission and distribution include high and low voltage grids, as well as district heating
rriers used as industrial feed stock (such as natural gas in chemical industry) are included as non
able energy carriers with corresponding CO
2
-emissions. Transportation by passenger cars i
with many different technologies, including hybrids, battery electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles
brids and internal combustion engine vehicles [6, 7].
Figure 5
Principal drawing of TIMES-Norway
TIMES-Norway – model description
TIMES (an acronym for The Integrated MARKAL-EFOM
System) is a bottom-up techno-economic model
generator for local, national or multi-regional energy
systems, which provides a technology-rich basis for
estimating energy dynamics over a long-term, multi-
period time horizon. It gives a detailed description of
the entire energy system including ll resources, energy
production technologies, energy carriers, demand
technologies and demand sectors. The model assumes
perfect competition and perfect foresight and is demand
driven. Thus the projected energy demand has to be
given exogenously to the model, and the TIMES model
aims to supply energy services at minimum global cost
by making equipment investments, as well as perating,
primary energy supply and energy trade decisions.
TIMES-Norway is developed by Institute for Energy
Technology (IFE) on commission of The Norwegian
Water Resources and Energy Directorate (NVE) and the
development st rted in 2008. The time horizon of the
model is from 2010 to 2050, with a flexibility of analysing
years within this frame. TIMES-Norway covers all onshore
energy use in Norway and the country is divided in five
regions with exchange of electricity between adjacent
regions and neighbouring countries.
The structure of the TIMES-Norway model is illustrated
in Figure 5. The demand for various energy services,
energy price information and resource costs and
availability are given exogenously to the model. On
the energy supply side, several conversion processes
are represented in detail; e.g. electricity and heat
production. Transmission and distribution include high
and low voltage grids, as well as district heating. Energy
carriers used as in ustrial feed stock (such as natural gas
in chemical industry) are included as non-subs itutable
energy carriers with corresponding CO2-emissions.
Transportation by passenger cars is modelled with many
different technologies, including hybrids, battery electric
vehicles, fuel cell vehicles, plug-in hybrids and internal
combustion engine vehicles [6, 7].