11
Position paper - CenSES 1/2015
2.2.Scenarios
The main scenario is the reference path, called REF. This scenario is based on present policies and decided
changes of the energy use of 2010. The population projection used in the reference path is the main middle
alternative published by Statistics Norway in 2012 [5]. The building regulation in force is “TEK10” and new
buildings are based on this regulation. In order to illustrate the uncertainty of the reference path, a few
alternative scenarios are analysed. Several other scenarios are of great interest and the intention is to continue
the work with more scenario analyses in 2015. The present work includes the following scenarios analysed with
TIMES-Norway:
REF
Reference path with the assumptions previously described. Based on present policies and decided
industry close downs/production increases. General energy efficiency measures are not included,
but the effects of present policies are included. Low energy and passive house standards are not
included. Battery electric vehicles (BEV) are restricted to maximum 50 % of passenger car demand.
REF-EE
Energy efficiency (EE) measures are available in TIMES-Norway and profitable energy efficiency will
be implemented. More efficient transportation results in a decreased growth of transport demand.
FROZEN
The objective of this scenario is to illustrate what would happen if the present energy system is used
to serve a growing population. Passenger cars are restricted to gasoline and diesel combustion cars
with improved efficiency of new cars. Buildings will not reduce energy use when refurbished and
the directive of energy labelling and lighting has no effect.
HIGH
The energy demand of industry is increased and there is no restriction of battery electric vehicles
(BEV).
LOW
Decreased energy demand of industry, possibilities to invest in energy efficiency measures,
decreased transport demand and higher energy prices (based on [8] and [9]).
Constant energy prices 2016 – 2050 are used in all scenarios but LOW. In scenario LOW, the development of
fossil energy prices and bio energy are based on WEO 2013 [8]. The electricity trade prices in LOW are
considerable higher compared to the other scenarios.
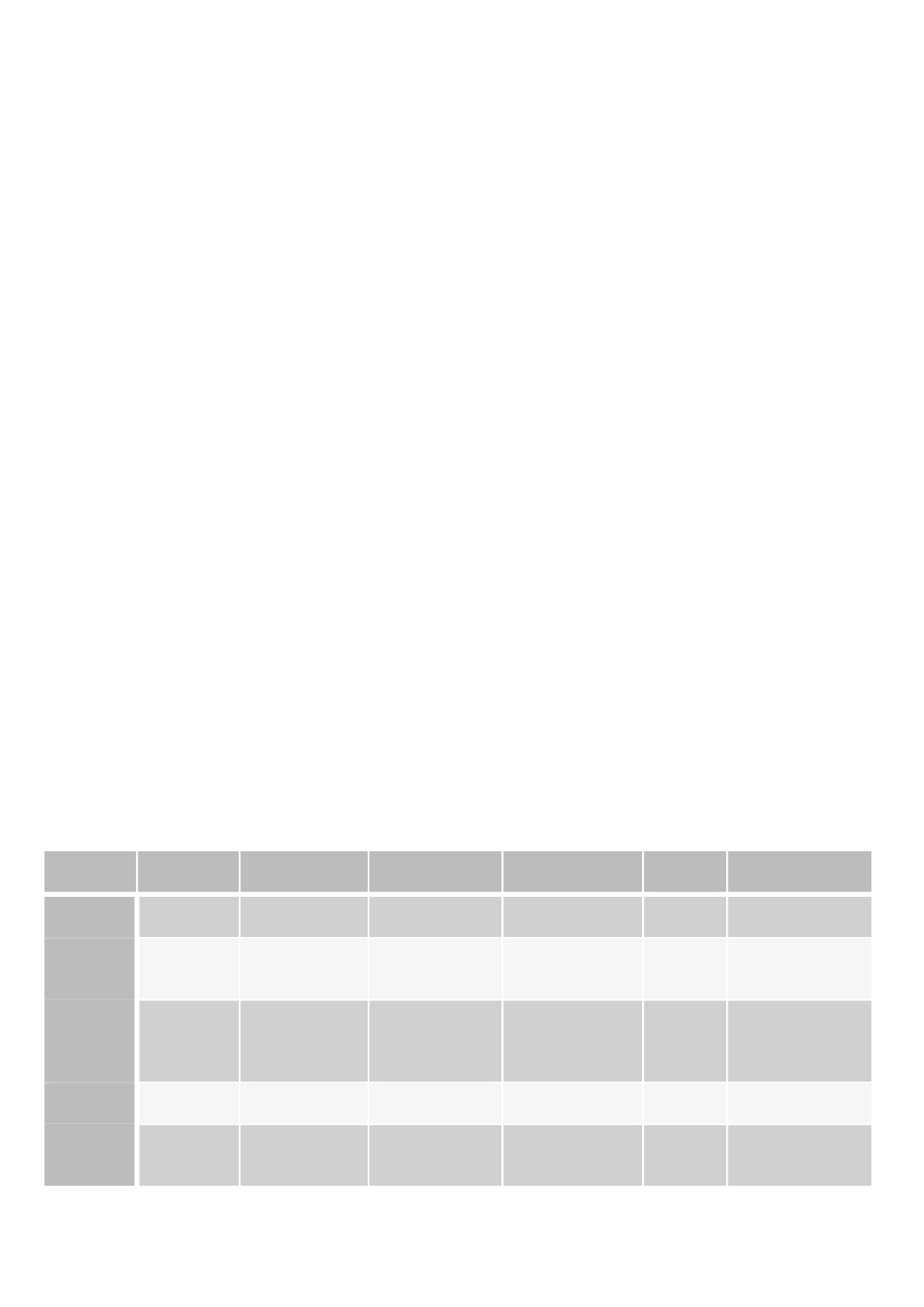
Table 2 Analysed scenarios with differences compared to the reference path of each demand sector
Scenario
Industry
Households
Tertiary
Transport
EE-
measures
Energy prices
REF
No
Constant 2016-
2050
REF-EE
EE
EE
EE
Less transport
demand (more
efficient)
Yes
Constant 2016-
2050
FROZEN
-
No effect of
renovations and
present
directives
No effect of
renovations and
present
directives
Present car types
No
Constant 2016-
2050
HIGH
Higher
activity
-
-
No restrictions
BEV
No
Constant 2016-
2050
LOW
Lower
activity
EE
EE
EE
Less transport
demand
Yes
Increasing 2010-
2050 (WEO2013)
3.2. Scenarios
The main scenario is the reference path, called REF.
This scenario is based on present policies and decided
changes of the energy use of 2010. The population
projection used in the reference path is the main
middle alternative published by Statistics Norway in
2012 [5]. The building regulation in force is “TEK10” and
new buildings are based on this regulation. In order
to illustrate the uncertainty of the refere ce path, a
few alternativ scenarios are nalysed. S veral other
sc narios are of great interest d th intention is to
continue the work with more scenario analyses in 2015.
The present work includes the following scenarios
analysed with TIMES-Norway:
REF
Reference path with the assumptions previously
described. Based on present policies and decided
industry close downs/production increases. General
energy efficiency measur s are not included, but the
effects of present policies are included. Low energy
and passive house standards are not included. Battery
electric vehicles (BEV) are restricted to maximum 50 %
of passenger car demand.
REF-EE
Energy efficiency (EE) measures are available in
TIMES-Norway and profitable energy efficiency will be
implemented. More efficient transportation results in a
decreased growth of transport demand.
FROZEN
The objective of this scenario is to illustrate what would
happen if the present energy system is used to serve
a growing population. Passenger cars are restricted to
gasoline and diesel combustion cars with improved
efficiency of ew cars. Buildings will not reduce energy
use when refurbished and the directive of energy
labelling and lighting has no ffect.
HIGH
The energy demand of industry is increased and there is
no restriction of battery electric vehicles (BEV).
LOW
Decreased energy demand of industry, possibilities
to invest in energy efficiency measures, decreased
transport demand and higher energy prices (based on
[8] and [9]).
Constant en rgy prices 2016 – 2050 are used in all
scenarios but LOW. In scenario LOW, the development
of fossil energy prices and bio energy are based on
WEO 2013 [8]. The electricity trade prices in LOW are
considerable higher compared to the other scenarios.
Analysed scenarios with differences compared to the r ference path of ach demand sector