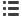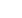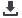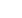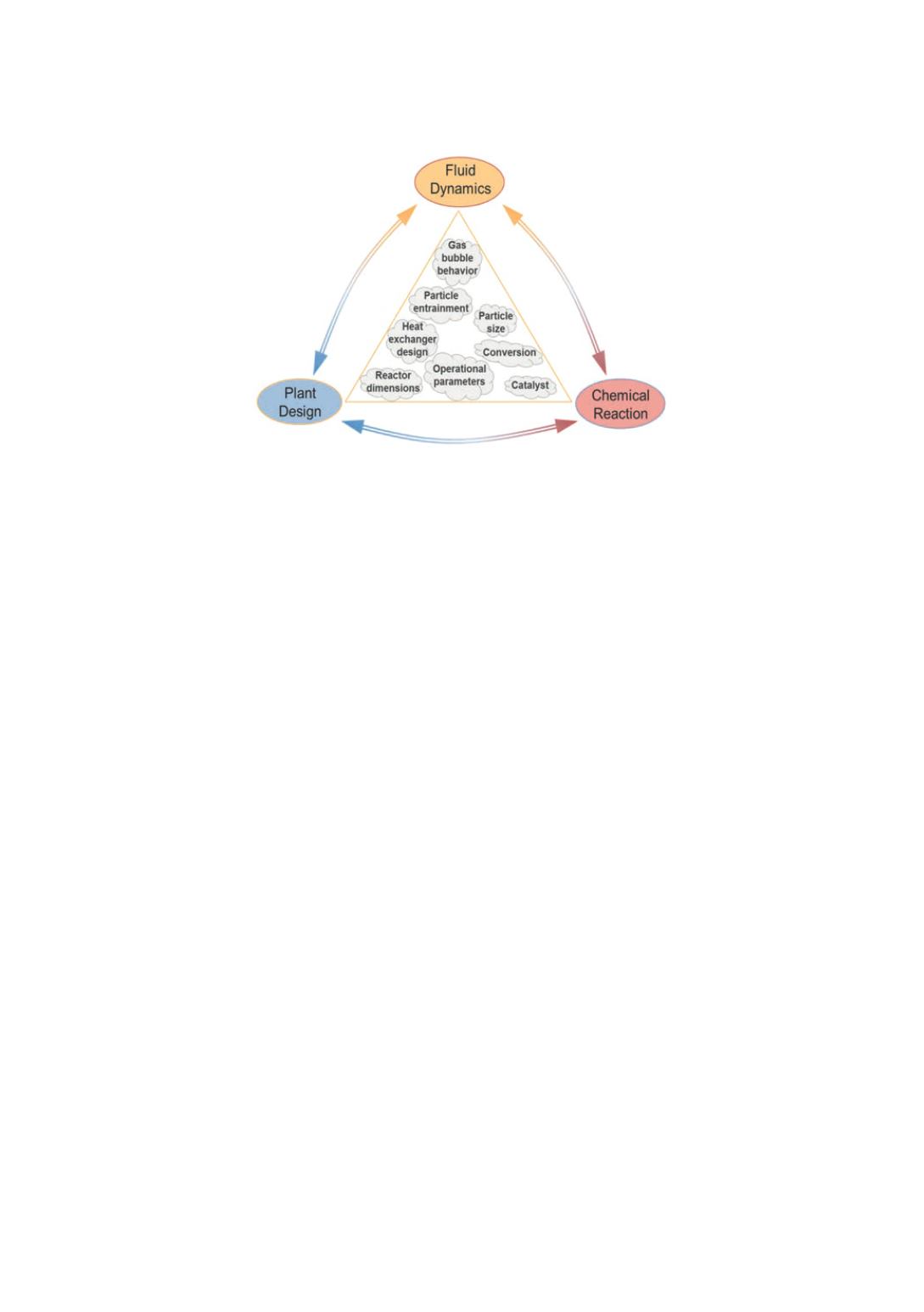
Figure 2
: Influence parameters on the Mueller-Rochow reaction
Basically, various commercial process simulation tools (also for solids applications) are
available. In the field of flow sheet simulation, ASPEN Plus
TM
, for instance, offers
various solids process modeling units that also comprise fluidized-bed reactors.
However, at present, it is not possible, using this tool, to fully describe the complexity
of the interactions between the different impact factors of the Mueller-Rochow
synthesis in detail. On the other hand, there are
c
omputational
f
luid
d
ynamics
simulation tools available, which are capable of describing fluid dynamics in great
detail. Despite great progress in computing capacities during the last years, it is still not
possible to employ this simulation tool for large-scale fluidized-bed reactors due to the
enormous computational effort required to simulate huge numbers of particles.
Hence, in order to meet all the complex and individual requirements, an own rate- based
model approach for the simulation of the Mueller-Rochow process was developed using
the
A
spen
C
ustom
M
odeler
TM
programming environment. Besides the opportunity to
create individual programming code, ACM also offers the advantage of access to
ASPEN property data banks, and, furthermore, the possibility of implementing user-
defined models in the ASPEN Plus
TM
environment, which can be connected to further
downstream processes in order to optimize the entire MCS process chain.
Experimental validation data from pilot plants
When developing a simulation tool it is crucial to have basic experimental data
available to validate the model equations. Therefore pilot plants are needed to provide
scalable and transferable data.
Pilot plant for fluid-dynamic investigations
Especially in the case of fluidized-bed pilot plants, certain requirements concerning e.g.
minimum diameter have to be considered to achieve significant and reliable data. For
investigating the fluid dynamics of the Mueller-Rochow reactor, a fluidized-bed pilot
plant was built in cooperation with Hamburg University of Technology (TUHH), with
a diameter of one meter and a total height of 5.4 meters, including a cyclone and a solids
recirculation system (see Figure 3 on the left). The pilot plant can be equipped with
different interchangeable internals. For the experimental investigations, the gas volume
flow and therefore the superficial gas velocities as well as the dense bed inventory were
159