000
4
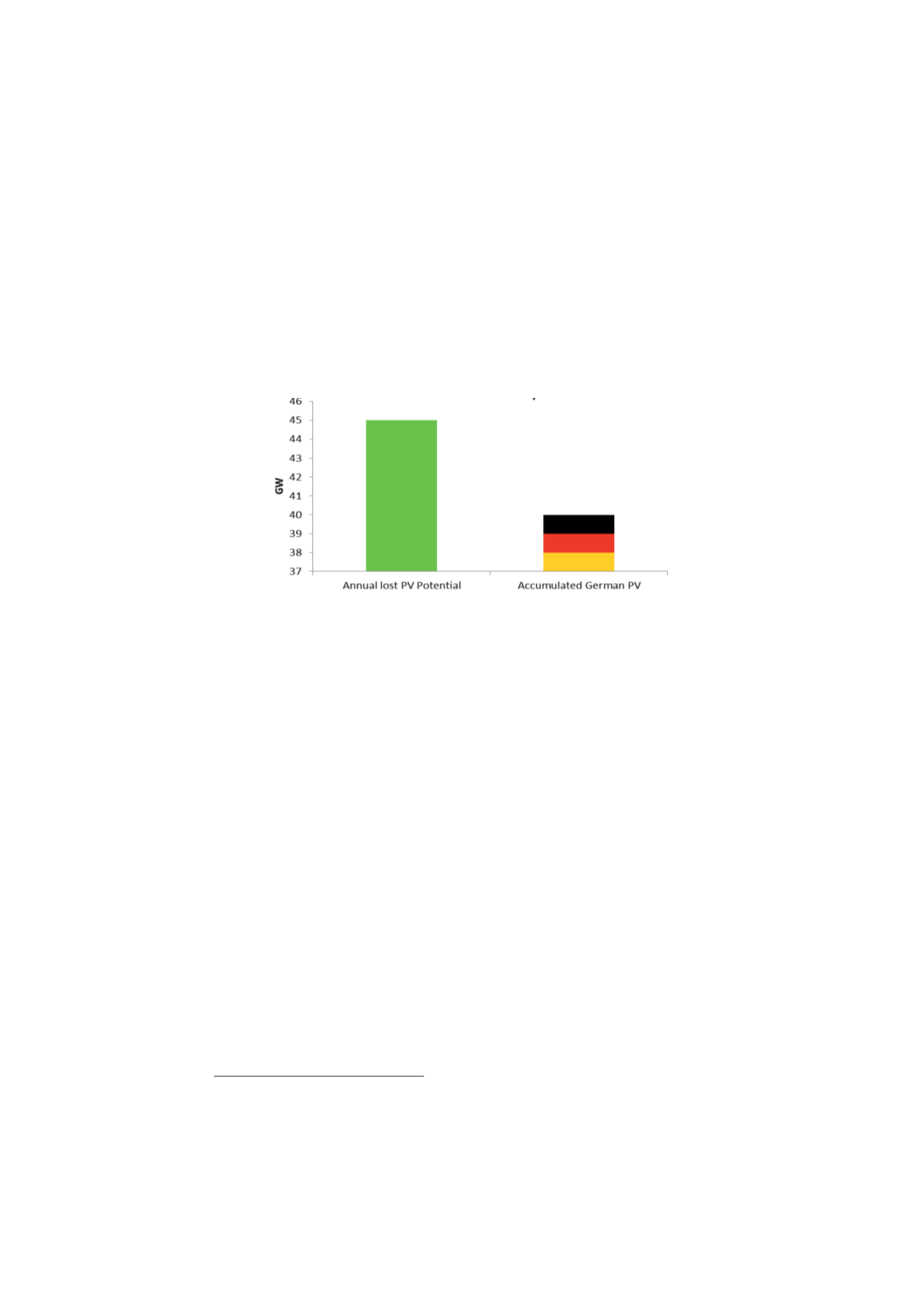
tons of grinding wastes and 150 000 tons of kerf wastes or a total of 300 000 tons
of wastes silicon and a conversion of 6 grams of silicon per watt, the total lost potential
solar power of this waste exceeds 45 GW per year. To put this in perspective, by the
end of 2015, Germany had cumulative installed PV capacity of just under 40GW
5
.
Therefore, every year more potential solar electricity is lost due to silicon wastes than
the entire cumulated PV output capacity of Germany.
Figure 3 Annual lost potential solar electricity vs. the accumulated solar installations in
Germany
Can the silicon wastes in the industry be recycled?
As previously mentioned, the wastes from the PV sector consist of two main
sources: undersize wastes from metallurgical silicon grinding and silicon containing
kerf wastes from wafer slicing operations. It should be noted that previous work on the
subject of kerf recycling has been focused on recycling kerf wastes, due to the high
purity of the silicon in this material, into a substitute for polysilicon, from which it
originates.
The dream of many during the time of high polysilicon prices was to take this waste,
separate it from the silicon carbide and PEG into which is was intricately mixed and
reuse it in ingot furnaces to make new ingots.
Below is a cursory review of previously published projects including one current
project, which follows or has followed the approach as described above, along with
some comments on each:
4
Which is then converted to polysilicon
5
https://www.energy-charts.de/power_inst.htm47