
Department of Chemical Engineering
Annual Report 2015
27
CO
2
CAPTURE FROM EXHAUST GASES AND
NATURAL GAS SWEETENING
The work we do involves all steps from theoretical
screening of new absorbents by use of computational
chemistry, through experimental screening, testing of
environmental
properties,
characterization
of
equilibrium, thermal properties, transport properties
and kinetics, degradation rates and mechanisms up to
testing in laboratory scale pilot plants. We have also
studied nitrosamine decomposition with UV-light on
pilot scale. In parallel with the experimental work we
develop models ranging from simple models for physical
properties to rigorous kinetic and thermodynamic
models, based on the electrolyte NRTL and extended
UNIQUAC model frame-works.
Below some examples of work, we are doing are shown.
The next figure shows measurements and model
representation of the reactions kinetics of LiOH, NaOH,
KOH and blends of hydroxide and carbonates.
PARITY PLOT FOR THE POHORECKI AND
MONIUK’S (1988) MODEL WITH REFITTED
PARAMETERS AND EXPER IMENTAL DATA.
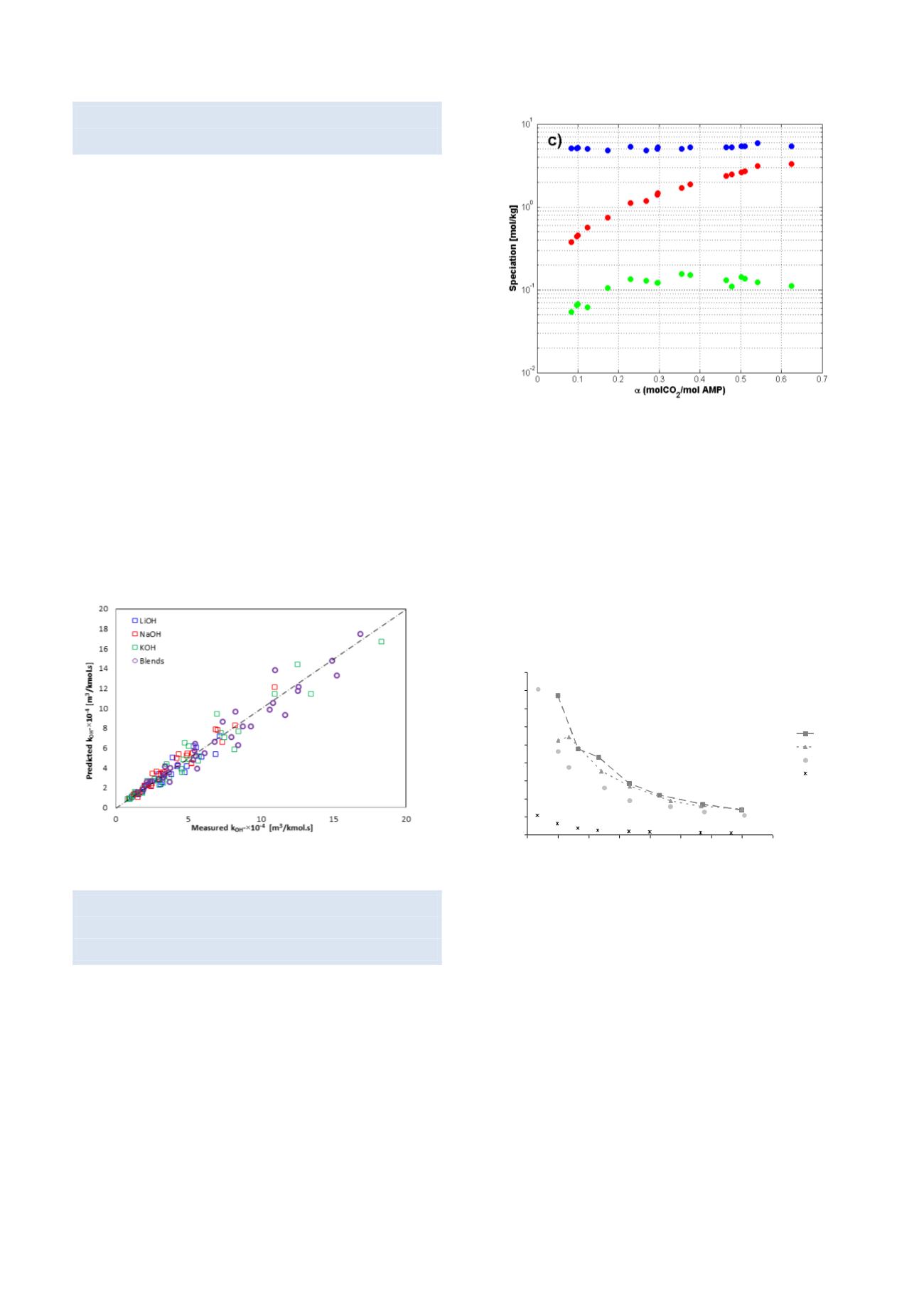
The figure below shows results from NMR
measurements in the CO
2
-loaded AMP system. For the
first time the formation of AMP-carbamate was reported
and the carbamate constant determined.
Liquid speciation determined directly by 13C NMR
spectroscopy for AMP-CO2-H2O system at: c) 45 °C.
,
AMP/AMPH
+
;
,
2
3
3
HCO / CO
;
, AMPCO
2
.
Degradation of absorbents is of great concern and we
work on identification of degradation products and
reaction mechanisms. In the figure below results from
oxidative degradation measurements show how the HEF
formation is compared to formate changes over time.
HEF/formate molar ratio for the experiments at different
oxygen concentration (21-98%) and temperatures (55-
75 °C).
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24
Time (days)
HEF/formate
21% O2 run2
50% O2
98% O2
21% O2 (75C)


















