reaction only takes place at the surface of NaCl crystals and the resulting NaAlCl
4
sticks to the
surface, thus leaving it unreactive. This results in long process times and a huge excess of NaCl
is needed.
Faster are reactions with organic compounds like urea
[2]
or imidazolium salts
[3]
which yield
ionic liquids. We found them to be scarcely soluble in the silane mixture and they can be easily
separated from it by phase separation techniques
[4]
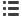
. Quenching of AlCl
3
can be monitored by
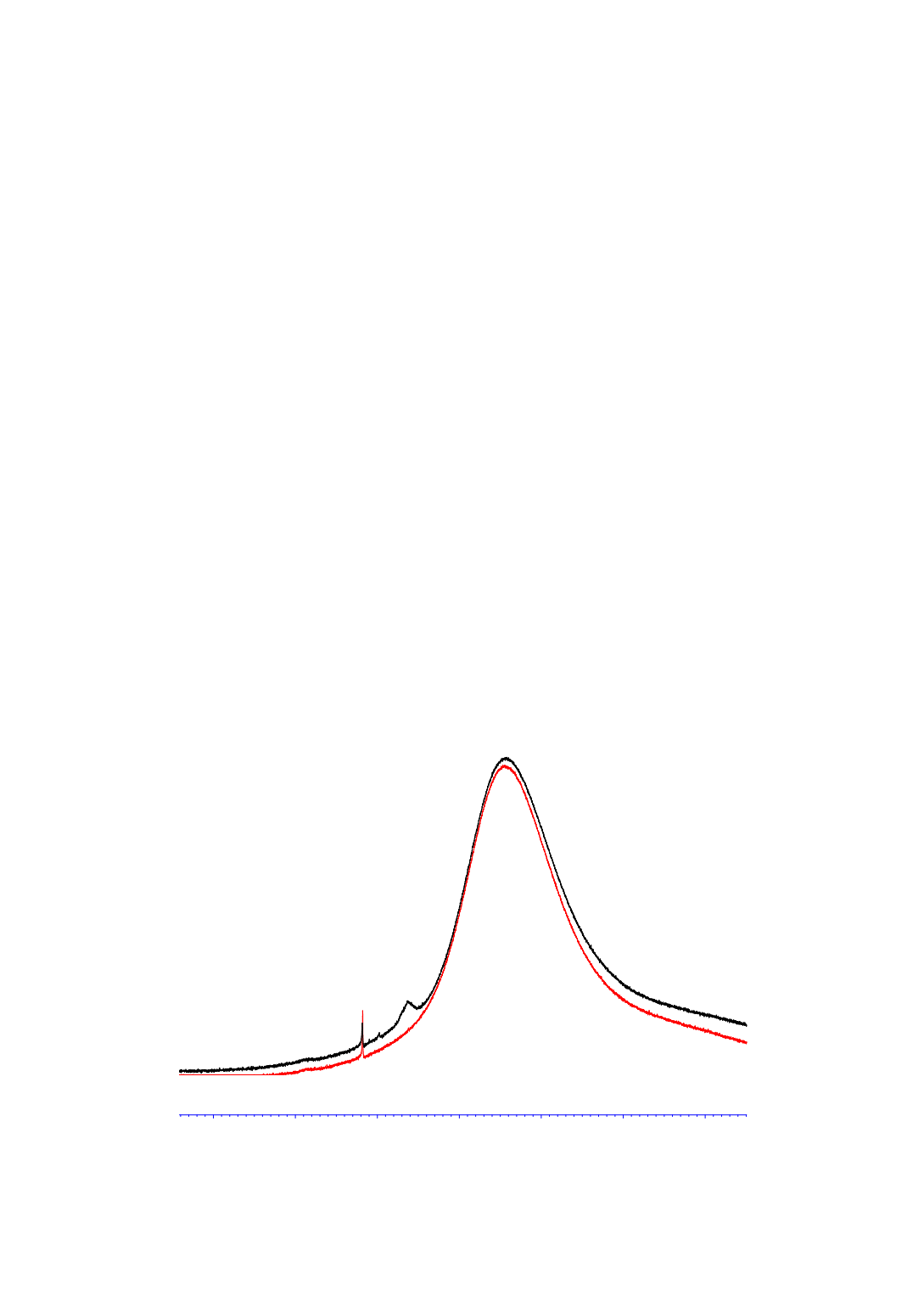
NMR in these cases (Figure 9). In one experiment, the aluminum concentration dropped from
160 ppm to 20 ppm in about 5 minutes when the product mixture of the direct synthesis was
stirred with 2,5 wt-% of methylimidazolium chloride. The remaining aluminum concentration
of 20 ppm was shown to correspond to the solubility of the resulting methylimidazolium
tetrachloroaluminate in the silane mixture. The signal at 102 ppm in the aluminum NMR could
therefore be assigned to tetrachloroaluminate.
Another way of preventing precipitation is blocking the reactions yielding tetrachloroaluminate.
This can be achieved by adding a strong aprotic Lewis base to the silane mixture which bonds
to the AlCl
3
firmly, thus preventing it from abstracting chlorine from chloroalkanes or other
compounds. Best suited for this are nitriles with high boiling points which are cheap and readily
available, like adiponitrile (Figure 10)
[5]
. It is sufficient to add these compounds to the silane
mixture at low concentrations of 150 - 2500 ppm because their reaction with AlCl
3
is fast and
complete. The formed complexes are considerably stable at all temperatures of the distillation
process and the high boiling point of any excess nitriles prevents them from contaminating
product fractions of the silane separation. The complexes and the nitriles remain in the high
boiling residue and are discarded.
Since tetrachloroaluminates are soluble in polar organic solvents, solids that have already
formed can be dissolved in aprotic high polarity solvents like tertiary amines and nitriles with
high boiling points, thus cleaning the metal surfaces of pipes and tubing
[6]
. This can be achieved
by pumping the solvent through the evaporators and tubing of the distillation equipment or after
disassembly of the same. Pumping it through a closed system prevents the formation of
hydrogen chloride by hydrolysis and is therefore preferable.
Figure 9:
27
Al-NMR of silane mixture before (black) and after treatment with
methylimidazolium chloride, broad hump from 20 – 120 ppm caused by probe and cavity
of the NMR spectrometer
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
ppm
MiniSpec -CopyrightCorporateAnalyticsWackerChemieAG
CurrentDataParameters
NAME 2893180E-LIMS
EXPNO
10
PROCNO
1
F2 -AcquisitionParameters
Date
25.02.2016
Time
14.13.07
INSTRUM
spect
PROBHD 5mmPABBOBB/
PULPROG
zg
TD
16384
SOLVENT
CDCl3
NS
1024
DS
4
SWH
52083,333 Hz
FIDRES
3,178914 Hz
AQ
0,1572864 sec
RG
575
DW
9,600 usec
DE
6,50 usec
TE
297,7 K
D1
1,00000000 sec
========CHANNEL f1========
NUC1
27Al
P1
10,00 usec
PL1
120,00 db
SFO1
130,3025348 MHz
F2 -Processing parameters
SI
32768
SF
130,302536 MHz
WDW
EM
SSB
0
LB
1,00 Hz
GB
0
PC
1,40
1DNMR plotparameters
CX
28,22 cm
CY
15,73 cm
F1P
148,296 ppm
F1
0,00 Hz
F2P
9,891 ppm
F2
0,00 Hz
PPMCM
4,90535 ppm/cm
HZCM
0,00000 Hz/cm
Integrale
AlCl
3
AlCl
4
-
145