24
Background
A growing population with an increasing economic
development and consumption leads to massive use
of the Earth’s resources (Rockström et al., 2009). Many countries and regions experience
water stress and ecological degradation of aquatic ecosystems, which is expected to further
increase and accelerate with climate change (Bates et al., 2008; IPCC, 2011; IPCC, 2014). Due
to global warming caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, an increased the
share of renewable energy production is needed, and large-scale investments in solar, wind
and hydropower are expected (IPCC, 2011). Reservoirs are also key-stones in the infrastructure
and prerequisite in water-stressed areas to secure adequate water-services to a large range
of sectors, and are used for the purpose of securing irrigation, drinking water supply, flood
control, navigation and more, as well as hydropower production.
The thesis will analyze how the design and operation of the reservoirs will affect water
consumption and the availability of water for various purposes, including irrigation,
drinking water supply and hydropower production. The study will be carried out using
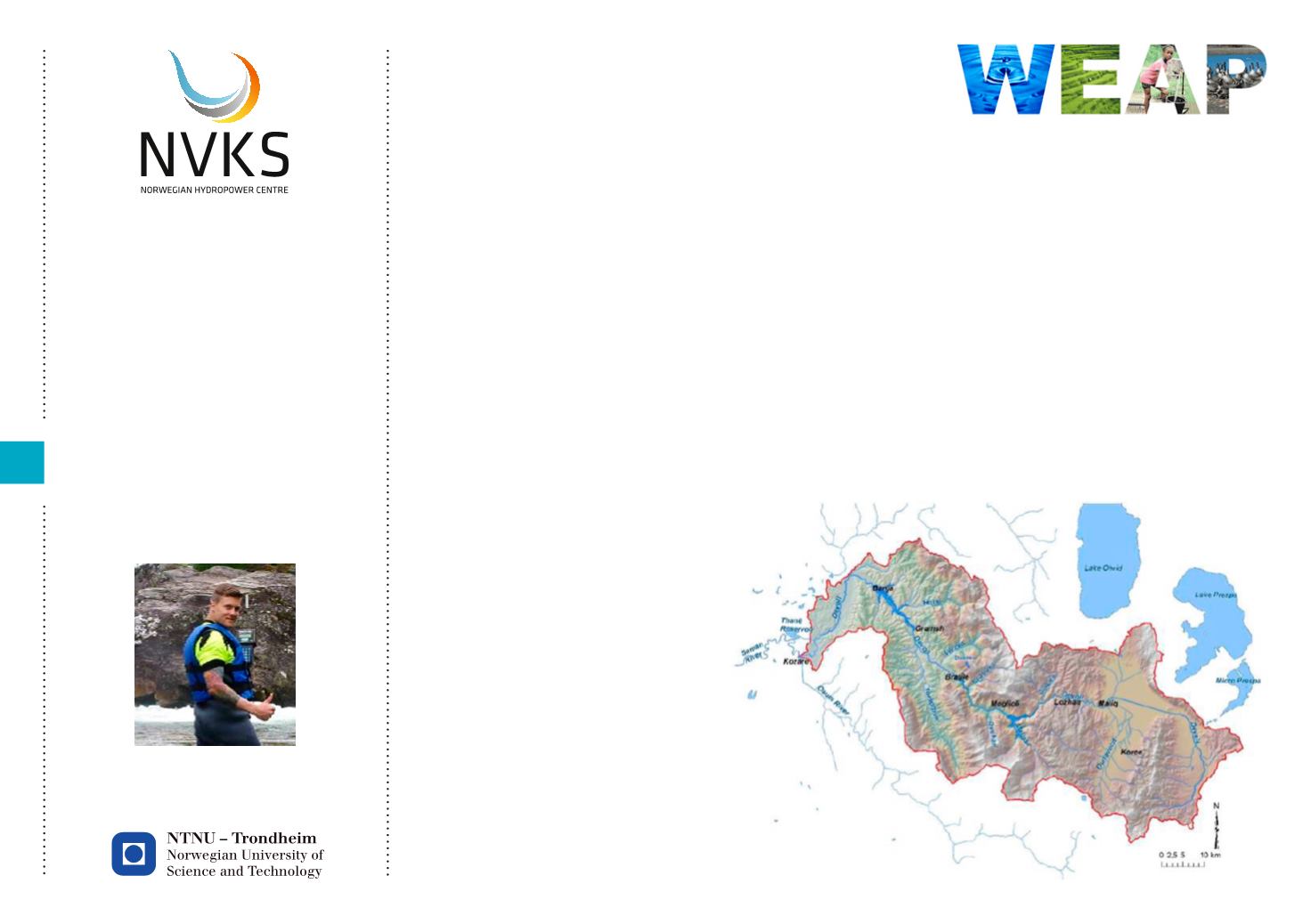
Devoll River Basin in Albania as a case, with an extensive on-going development with
Norwegian ownership involved
(Statkraft). A hydrological model
of Devoll River Basin will be
constructed using the Water
Evaluation and Planning (WEAP)
software tool. Future possible
scenarios will be simulated and
analyzed in WEAP to assess the
impacts of climate change, and
change in water consumption
and demands due to population
growth, improvements in
technology and different policies
for water allocation.
Master Thesis
Department of Hydraulic and
Environmental Engineering
Modelling of Water
Allocation and Availability in
Devoll River Basin, Albania
By Christian Almestad
Supervisor: Knut Alfredsen
Tor Haakon Bakken