
77
Department of Electric
Power Engineering
Spring 2017
Analyses of Reserve
Procurement Costs
Using the EMPS Model.
Case Study Norway
2050.
Supervisor:
Hossein Farahmand
Co-supervisor:
Arild Helseth
In cooperation with:
SINTEF Energy
Tale Marie Astad Paulshus
Background
An increase of generated power from
intermittent renewable energy sources in
Europe will result in a more unpredictable
generation schedule and increase the need
for reserve power. The master project concern
reserve procurement costs and has as goal to
extract data from simulations to analyse prices
related to reserve requirements for a scenario
of Norway 2050. The contribution of the master
project will be to provide information for decision
takers to utilize the Norwegian hydro resources
for a future power system.
SINTEFs EMPSmodel will be used as simulation
tool for the master project. The EMPS model is
a power market simulation tool with the goal
of maximizing the socioeconomic benefit of a
power system based on the water value method.
The model is designed for stochastic
optimization of the Nordic power system, which
includes stochastic handling of hydro inflow. The
Norwegian power system connected to Europe
will be represented in a simplified way. The
data set for Norway is provided by SINTEF and
projected towards 2050 by the student. Wind and
solar series are added to represent the variation
of intermittent generation during the year.
As themodel of the power system is represented
in a simplified way, more nodes and links can be
added to make the model more representative
for the real power system. A higher level
of detail of the data set may be obtained by
including wind and solar series specific for the
geographical areas represented by the nodes in
the extended model.
MASTER THESIS
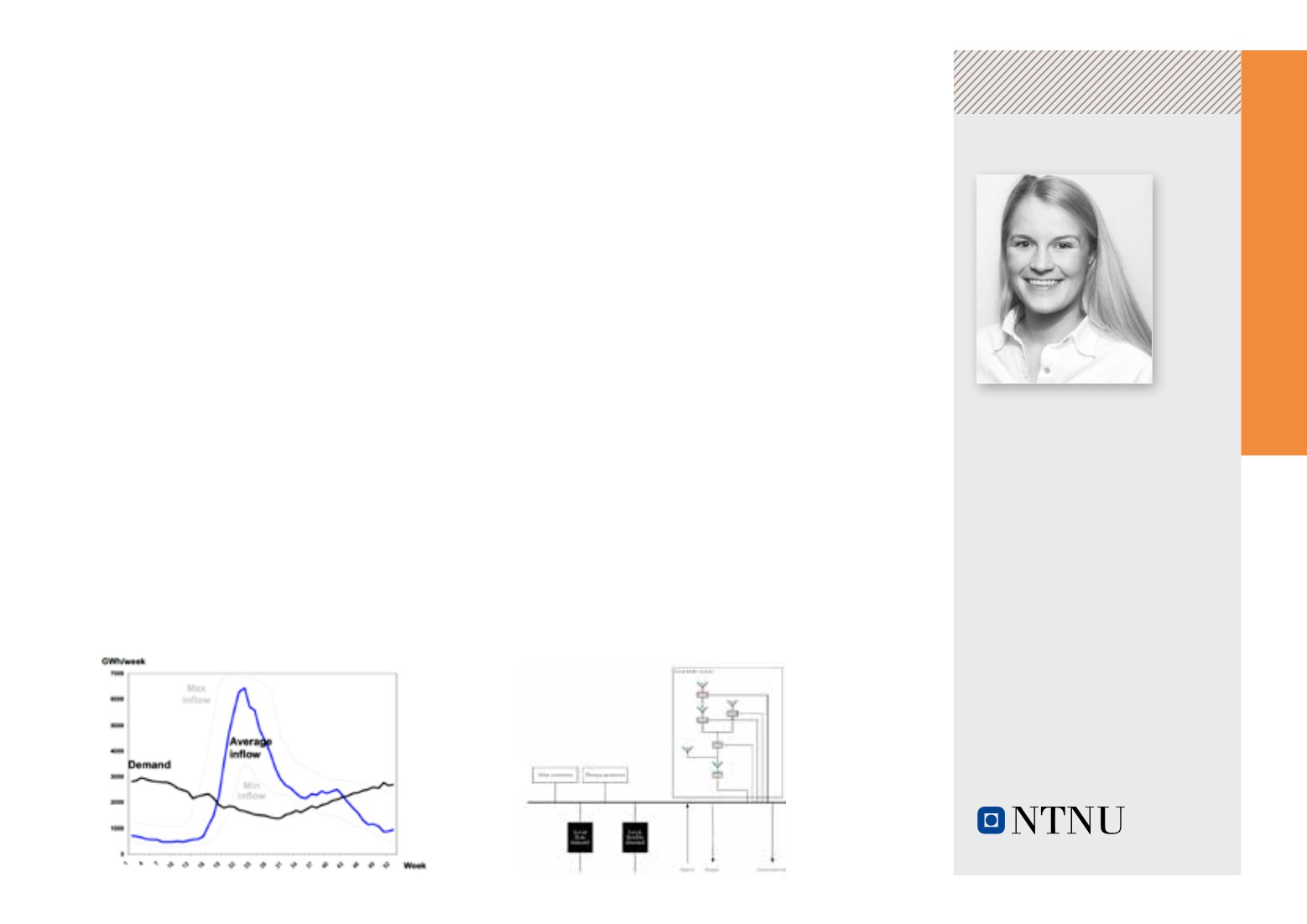
Hydro inflow and
demand in Norway
during one year
Local area model
in the EMPS model
Source:
Compendium
ELK-15
Hydro power
scheduling,
NTNU
Source: Manual of
the EMPS model,
SINTEF Energy
















