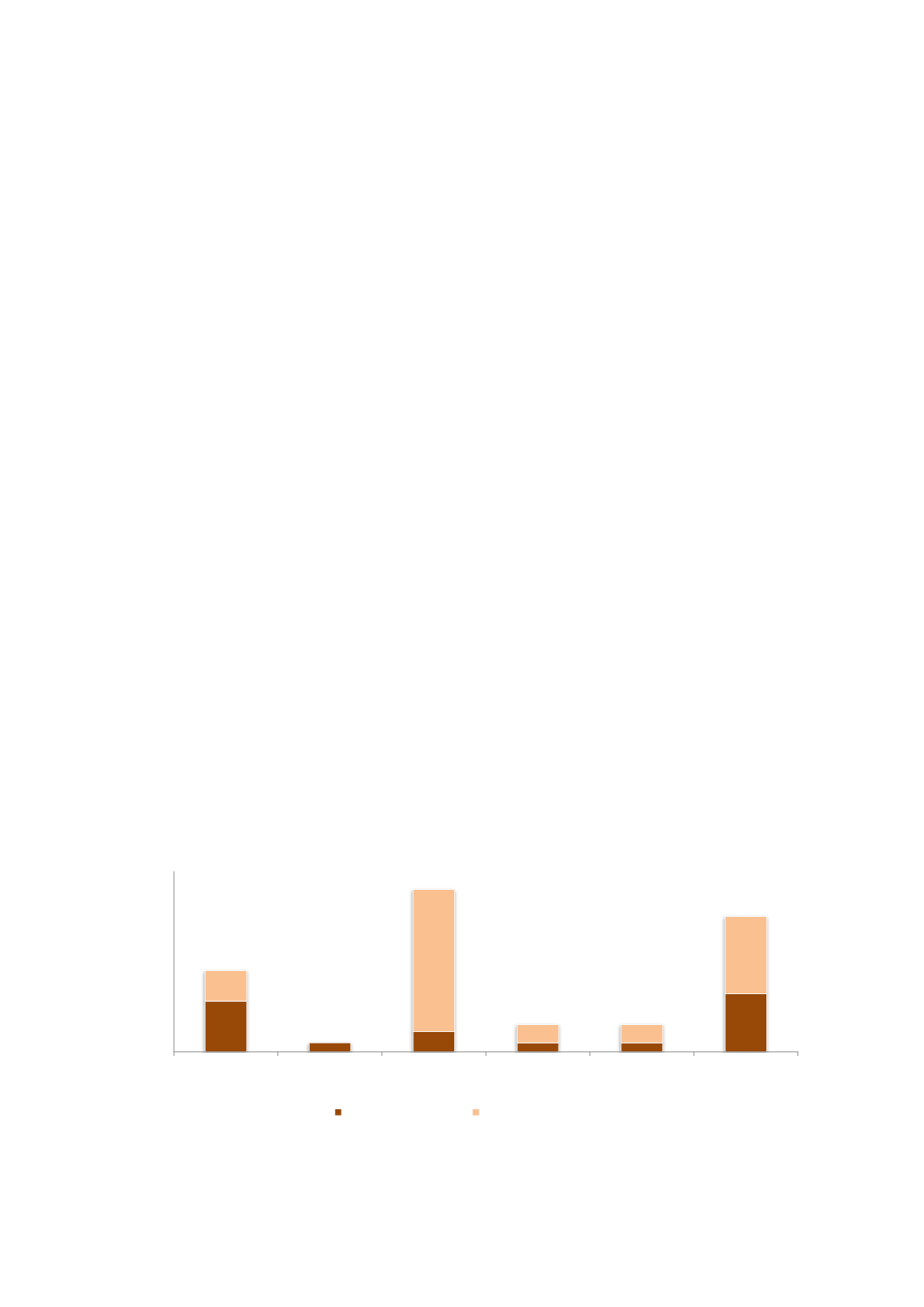
16
The manufacturing and use of PV modules is associated with a number of different steps. Firstly the
conversion of light to electricity requires high purity materials. Silicon is the dominant material. Silicon
is then molten into large crystal blocks (ingots) and sawn into thin wafers. These wafers are then
chemically treated in a cell process and assembled into modules. Finally modules are installed and
integrated into the electricity system (or used in off-grid applications). For our purposes we include
the following categories of actors along the supply chain: (1) raw-material production, (2) ingots and
wafers, (3) system, (4) machinery & equipment (5) investment & finance and (6) consultancy & R&D.
A number of actors deliver production equipment and services along this supply chain. While 1-3 are
associated with particular steps along the supply chain actors associated with group 4-6 may supply
products and service to all levels.
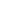
Fro
m figure 5-5 we can see that most of the firms are placed in three categories: Rawmaterials, system,
and consultancy and R&D. Firms producing raw materials produce primarily silicon though some also
produce other materials important to the PV industry. System firms are firms that are connected to
the process of installing PV systems, mostly on business buildings and private homes in Norway. There
is only one firm in our set of responses that produce wafers and ingots, and no firms that currently
produce modules in Norway. When we consider only firms that have made significant investments in
PV, we can see that the majority of these firms produce raw materials and deliver consultancy and
R&D services. The large group of system firms mostly dedicate less than five full-time equivalents to
PV.
Similarly to OWP, there is a broad variety within each PV category. For instance, in the raw materials
category there are firms supplying products and technology ranging from electrical conductive
adhesive (glue) to silicon and silicon carbide.
Figure 5-5 Number of firms across the PV supply chain
Source: Survey data and desktop research
0
5
10
15
20
Raw materials Ingots and wafers
System
Machinery &
production
Investments &
finance
Consultancy and
R&D
Number of firms
5 or more FTEs on PV Less than 5 FTEs on PV