45
ZEB
annual report 2015
and doors. However, to fully evaluate the
real performance of a building component,
exposure to real climatic conditions is
necessary. This can be achieved in the ZEB
Test Cell Laboratory.
The Test Cell Laboratory can be used for
research, development, and testing of low-
energy, integrated building systems under
realistic operational conditions. The laboratory
is made of two test rooms, each one
surrounded by a control volume. Each room
has one surface exposed to the outdoor, so
that different building envelope technologies
can be tested in parallel, side by side. In
addition to comparative and calorimetric tests
on building materials and building envelopes,
the Test Cell Laboratory is a technical
development facility where different building
equipment and terminals can be tested and
optimized, together with their control systems,
in combination with building envelope
components.
Contact: Francesco Goia and Einar Bergheim.
Facility for user-technology interaction
studies “ZEB Living Laboratory”
The “component” often having the most
influence on the energy use of a building is
the user. A building laboratory is therefore not
complete without facilities for evaluation of
how different users interact with the buildings
and its technologies and how this interaction
influences energy use.
The ZEB Living Laboratory is a test facility that
is occupied by real people, who are using the
building as their home. The focus is on the
occupants and their use of innovative building
technologies, such as the intelligent control of
building services, interactive user interfaces
and interplay with the energy system as a
whole.
The ZEB Living Laboratory is at the same time
used to study various technologies and design
strategies in a real world living environment:
• User centered development of new and
innovative solutions: the test facility is used
within a comprehensive design process
focusing on user needs and experiences.
• Performance testing of new and existing
solutions: exploring building performance in a
context of realistic usage scenarios.
• Detailed monitoring of the physical behavior
of the building and its installations as well as
the users’ influence on them.
ZEB researchers within the fields of
architecture, social science, materials science,
building technologies, energy technologies,
and indoor climate jointly study the interaction
between the physical environment and the
users. The ZEB Living Laboratory is important
in making sure that the solutions developed
within ZEB Centre are tested and verified
at an early stage. The Living Laboratory
strengthens collaboration between industry
partners and researchers.
Contact: Thomas Berker, Ruth Woods and
Hans Martin Mathisen.
The next step: ZEB Flexible Laboratory
ZEB Living Laboratory and ZEB Test Cells
Laboratory allow development and research
on systems and technologies for smaller
buildings. A laboratory facility for testing of
full-scale integrated systems for zero emission
commercial and public buildings in a Nordic
climate is not yet available. The ZEB Flexible
Laboratory will be such a facility.
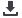
Figure 1. The figure shows a panorama view of building physics laboratory with rotatable hot box (grey
box to the right), climate simulator (blue box in the middle), and RAWI box (rain and wind box, to the left).
Photo: SINTEF Building and Infrastructure.