
49
Annual Report 2016
SAMCoT
ICE MANAGEMENT AND DESIGN PHILOSOPHY
Ice management (IM) is defined as the sum of all activities carried out with the objective of mitigating hazardo-
us situations by reducing or avoiding actions from any kind of ice feature (sea ice or glacial ice), and includes
several types of barriers. The scope of IM activities is wide. It covers many aspects including technologies,
equipment, systems, processes, operational procedures, etc.
METHODS FOR MODELLING ICE
MANAGEMENT BARRIERS
MIM-
Prediction
MIM-
Disconnect
Drilling program
Minimum alert time/
Termination time
Managed
Rapid
Emergency
MIM-
Prediction
MIM-
Ice Breaking
MIM-
Disconnect
Drilling program
Minimum alert time/
Termination time
Managed
Rapid
Emergency
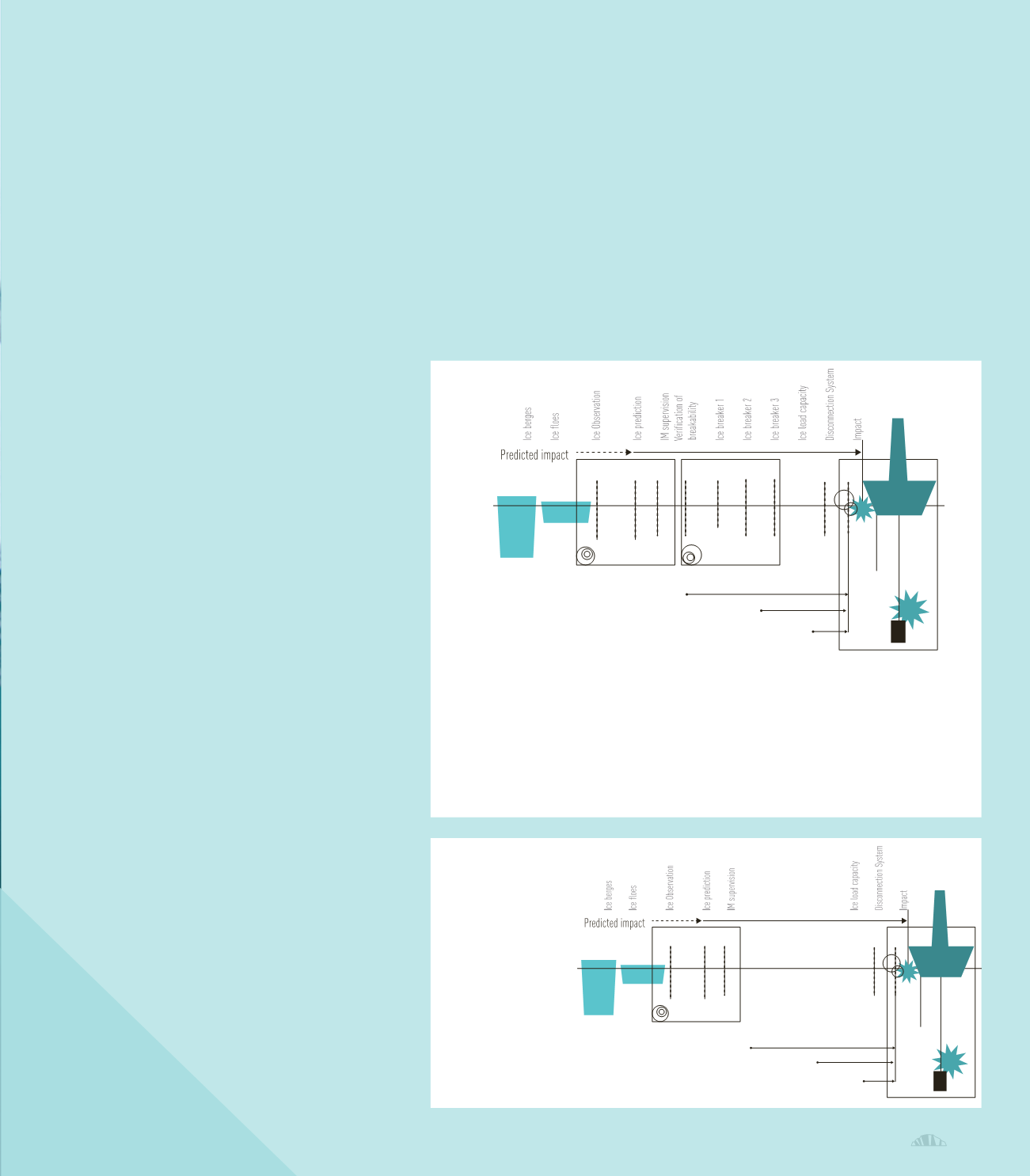
Case B: Extreme arctic condition with active fight IM by means of ice breakers. Vertical dotted lines illustrate ice management barriers. The overall
objective of ice management is to avoid contact between ice and the protected unit (e.g. drilling rig). If the probability of ice contact is high,
the protected unit shall be relocated, either by a managed, rapid, or emergency disconnection procedure.
Extreme Arctic conditions with active fight IM by means of ice breakers. Vertical dotted lines illustrate ice management barriers. The
overall objective of ice management is to avoid contact between ice and the protected unit (e.g. drilling rig). If the probability of
ice contact is high, the protected unit shall be relocated, either by a managed, rapid, or emergency disconnection procedure.
Workable conditions with semi-
active flight IM (Probability of de-
tection (POD) of ice floes/ice bergs)
The overall IM approach is based on
disconnection of the protected unit
if ice is detected and forecasted
to be approaching. No physical ice
management with icebreakers is
included.
Types of Barriers:
●
Ice detection and observation
●
Ice prediction
●
Ice management supervision (alerting and decision)
●
Verification of ice breakability
●
Physical ice management with icebreakers
●
Disconnection procedures and systems of the protected unit
The industry has already been involved in different IM
activities for a long time and in several geographical
areas. Literature refers to different types of challenges.
Different companies and disciplines have different roles,
responsibilities, priorities, technologies, terminolo-
gies and cultures and have different views on how to
approach IM issues.
Researcher Stian Ruud started to work with these issues
from the beginning of his engagement in SAMCoT in
2016. Ruud led two industry workshops in Trondheim,
hosted by SAMCoT, where industry partners presented
their different views on IM topics. During the workshops,
participants discussed the need for modelling IM bar-
riers. As a result, Ruud’s research activity was defined.
In collaboration with other WP5 researchers, he aims to
provide quantitative and qualitative methods for model-
ling ice management (MIM) barriers, by implementing a
top-down ‘method for supporting IM decisions’ based on
aggregated quantified and qualitative information.
The modelling approach is also based on international
standards like ISO/DIS 35104 on IM and the ISO/DIS
19906 standard and regulations on barrier management.
The extensive work done in 2016 will enable Ruud to
write a new report in 2017: ‘Methods for IM barrier
modelling (MIM)’. Two different case scenarios/studies
will be carried out as illustrated in the figures:
















