CenSES annual report 2014
16
Work related to the Work Packages in RA2
The activities of RA2 are in a wide spectre related to energy
systems and markets. The research is ranging from analysis
of details in the energy system or in the electricity mar-
ket to analysis of global energy systems. Research groups
from CenSES have been actively involved in the analysis
performed by the European Energy Modeling Forum (EMF)
and in IEAs Energy Technology Systems Analysis Program
(ETSAP).
In WP1 on Modelling technology learning in energy
systems we made an e ort to establish a common Censes
Energy Database (CED); however it has been decided that
this work has to be extended into a national technology da-
tabase in cooperation with both CenSES and CREE partners.
Establishment and operation of national energy database
will require national funding.
The research in WP2 on Energy demand and energy e -
ciency has been related to making a new energy projection
towards 2050. A detailed study has been performed to be
able to develop a baseline projection and alternative sce-
narios for future energy demand in Norway. The work with
the Position Paper “Norway´s role as a exibility provider in
a renewable Europe” has been presented at Technoport Talk
in Trondheim, and at a
«
Klimafrokost
»
arranged by Norsk
RA 2 Energy Systems and Markets
Klimastiftelse in Oslo. The work with the Position Paper
“CenSES-Energy demand towards 2050” has been present-
ed at the RERC2014 conference in Oslo, and at the ETSAP
workshop in Beijing.
The relation between energy economists and the develop-
ment of energy policy, and the impact of socio-economics
on energy policy and energy demand has been studied
thoroughly.
In WP3 Including new functionality in energy system and
market models a variety of energy system and market mod-
els have been used by researchers and PhD-students. The
research has been focused on improvement of the models.
Two new energy system models have been developed;
EMPIRE and MultiMOD. EMPIRE is a long-term investment
model for energy systems where the impact of short-term
variability on long-term investments in energy production
is included. The MultiMOD is an equilibrium model that
includes a large number of alternative fuels.
In WP4 E ects of global policy on regional energy systems
the main research has been in related to the LinkS-project.
In 2014 a study for the Zero Emission Platform (ZEP) was
carried out focusing on renewable energy technologies and
storage to achieve emission reduction.
The European power system is expected to become more
integrated and include a larger share of intermittent
renewable production. This development is driven by EU
environmental targets and ambitions. In Norway, new
cables to Europe, tighter market coupling and increased
contributions from intermittent production is expected to
give increased price volatility, larger volumes and higher
prices in balancing markets. This will increase the impor-
tance and pro t potential of a consistent view on trade in
all short-term markets. The producers’ ability to optimally
bid their resources in a broad and complex range of mar-
kets is a premise for the e cient utilization of Norwegian
hydropower resources and the ability to provide balancing
exibility to the system.
Hydropower producers need to schedule when to release
water from reservoirs and participate in wholesale electricity
markets where the day-ahead production is physically
traded. A mixed-integer linear stochastic model for bid op-
timization and short-term production allocation has been
developed and tested through a simulation procedure
implemented for a complex real-life river system. The new
stochastic bid model sees uncertainty in both spot market
prices and in ow to the reservoirs. The same simulation
procedure has also been implemented for a practice-based
deterministic heuristic method similar to what is currently
used for bid determination in the industry, and the results
are compared.
The stochastic approach gives improvements in terms of
higher obtained average price and higher total value than
the deterministic alternative. This approach also performs
well in terms of startup costs. In the presence of river ow
travel delay, the practice-based method is even more out-
performed by the stochastic model.
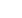
Development of a bidding Model for a Multi-reservoir Hydropower system