
Background
Hydraulic turbines are used extensively to stabilize
power grids because they can restart rapidly
and/or change the power output before the grid
collapses completely or black out. In recent years,
a dramatic increase in grid-connected wind and
solar power has resulted in problems related to
power grid stability and reliability. Operating life
of the hydraulic turbines has been affected. The
runner blades experiencemore fatigue.
Current work
Present work is related to the series of
Francis-99 workshops, which are organized
by NTNU and LTU. I am needed to perform
experimental and numerical investigations on
the model Francis turbine. The experimental
investigations include both, steady state and
transient measurements. The work also
focuses on fluid structure analysis on the
Francis runner. Under this work, two-way
coupling simulations will be performed.
The following objectives have been defined:
•
CFD and mechanical analysis of the Francis turbine.
•
Investigate the fatigue loading on the runner blades.
•
Investigate the consequences of rotor stator
interactions.
•
Investigate the effects of added mass on the runner
natural frequency.
Department of Energy and
Process Engineering
2014-2017
Fluid Structure Analysis
of a Model Francis
Turbine
Supervisor:
Ole Gunnar Dahlhaug
Chirag Trivedi
POSST DOC.
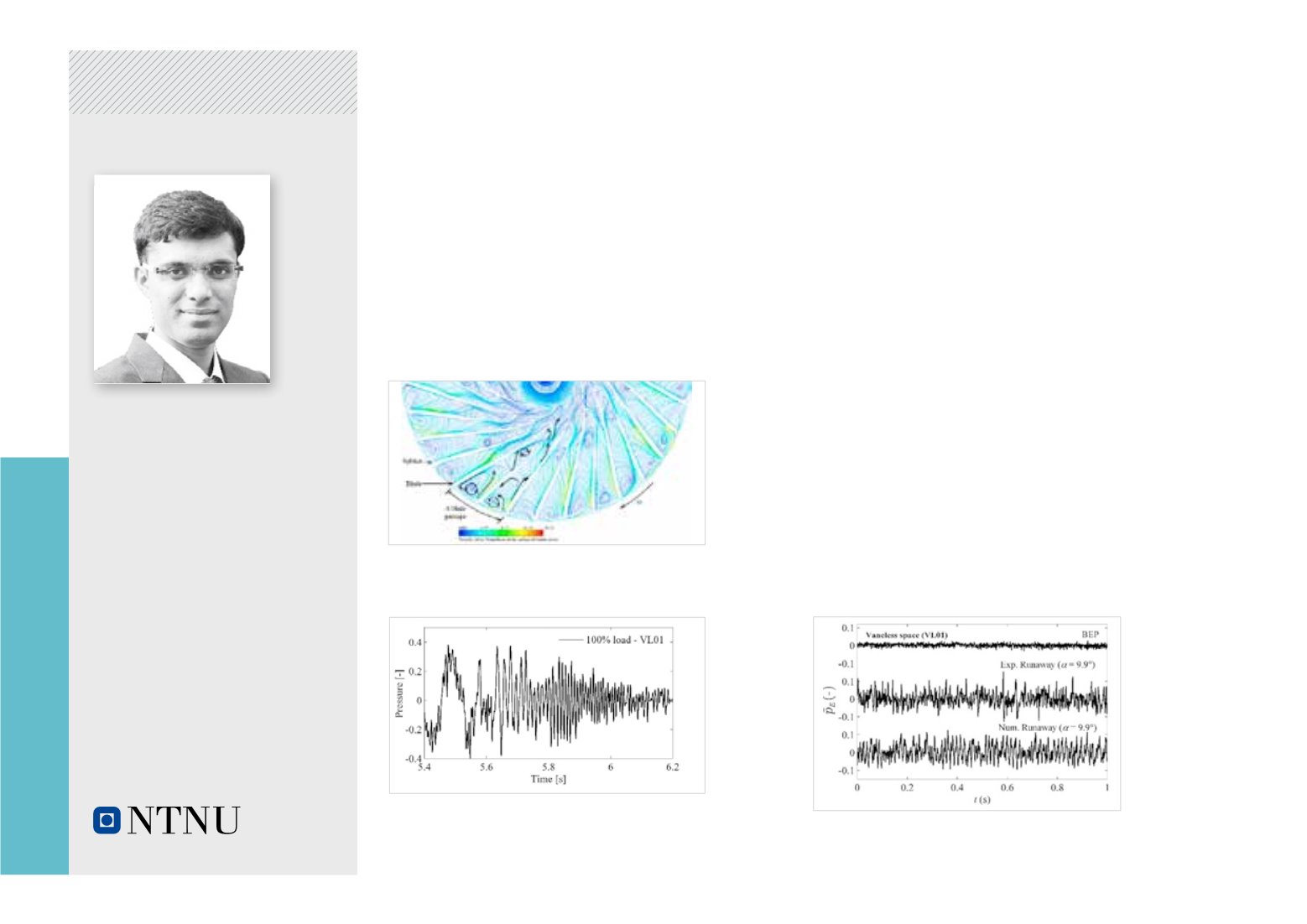
Swirling flow inside the blade passages during run-
away operating condition of themodel Francis turbine
Unsteady pressure variation/pulsations in the vaneless
space during transition from steady state full load
operating condition to the total load rejection of the model
Francis turbine
Pressure pulsations developed in the vaneless space
during the best efficiency operating point (BEP) and
runaway condition
64
















