Basic HTML Version

118
3.1.4. Polyelectrolyte effects:
solubility
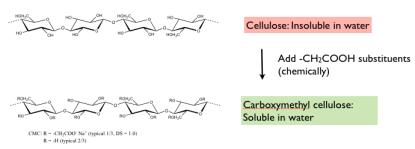
Introducing charges on a polymer has pronounced effects on solubility. For
example, water-insoluble cellulose becomes water-soluble upon adding about
0.7 or more carboxyl groups per glucose residue, i.e. for a degree of
substitution DS > 0.7.
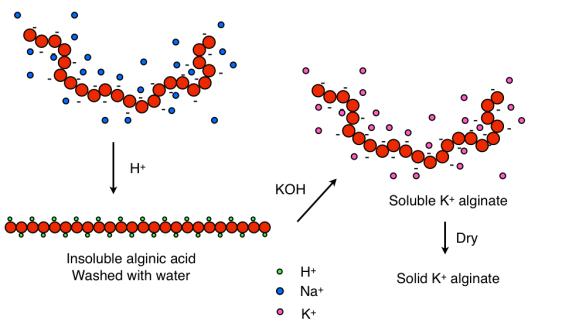
Another example is alginates, most of which are water-soluble when pH is
above 3.5, but they precipitate out of solution when most of the carboxylate
groups (-COO
-
) become protonated (-COOH) and the alginate looses its
polyelectrolyte character. This was utilized in Section 3.1.3. above.
Polycationic chitosans precipitate from aqueous solutions when the charged
amino group (-NH
3
+
) deprotonates into –NH
2
, resulting in a neutral polymer. In

