Basic HTML Version

39
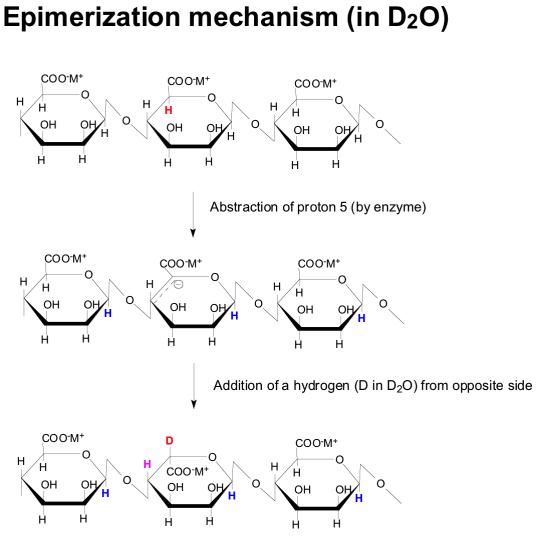
deuterium becomes incorporated at C5 in all G residues. D is “invisible” in
1
H-
NMR. This is in fact a proof for the mechanism of epimerization (figure below)
1.2.13. Epimerization: Macromolecular
consequences
Epimerization of M residues (into G) has a tremendous influence on the
properties of the alginate. Properties that change upon epimerization include:
•
Gelling with Ca
++
and other divalent ions
•
Solubility at low pH
•
Interactions with other molecules, for instance receptors of the innate
immune system.
Figure 17. The mechanism of epimerization

