Basic HTML Version
87
The terms M
n
, M
w
and M
z
are sometimes written with a bar, as in
M
w
. In this
compendium the bar is omitted as the subscript clearly indicates a molecular
weight average. Note that M
w
should not be used as an abbreviation for the
word ‘molecular weight’, but MW is OK.
2.1.7. DP averages
DP averages (and distributions) are equivalent to molecular weight
distributions. Interconversion is simple:
M
n
=
M
0
DP
n
M
w
=
M
0
DP
w
M
z
=
M
0
DP
z
2.1.8. Continuous distributions
Since the number of monomers in a chain normally is an integer, and
distributions hence are discrete, the size of the chains and with of the
distributions makes it more practical to use continuous functions and graphical
presentations:
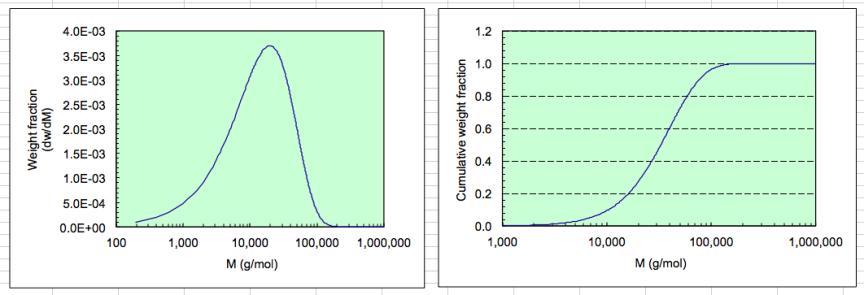
The figure on the left shows the weight fraction as a function of the molecular
weight (M). Note that a logarithmic scale is used for M. Such a figure is
commonly used. The figure on the right shows the cumulative distribution. It is
useful to determine the amount of material (weight fraction) above or below a
certain M (or DP). For example, in the figure a M of 20.000 (arrow)
corresponds to a cumulative weight fraction of 0.3, meaning that 30% of the
mas has a molecular weight lower than 20.000.

