Basic HTML Version

58
-
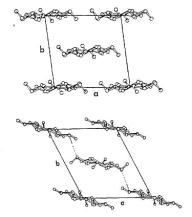
Antiparallel chains
-
Slight tilting of the chains
-
Stabilizing H-bonds between the layers
Hence, cellulose II is a thermodynamically more stable form than cellulose I.
The latter is therefore metastable.
1.4.7. Cellulose
solvents
Cellulose is, as already mentioned, completely insoluble in water. Certain
solvents dissolve cellulose, including:
•
Cadoxen: [Cd(en)
3
](OH)
2
•
CED (Cuen)
20
: [Cu(Ethylene diamine)
2
](OH)
2
Both cadoxen and cuen are strongly alkaline. This facilitates dissolution
(why?), but the cellulose degrades quite fast.
•
Dimetylacetamide/LiCl. A relatively new, non-aqueous solvent, much
used e.g. as solvent for molecular weight analysis.
•
Ionic liquids, e.g. 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMIMCl), 1-
ethyl- 3-methylimidazolium chloride (EMIMCl), 1-butyl-2,3-
dimethylimidazolium chloride (BDMIMCl), 1-allyl-2,3-
dimethylimidazolium bromide (ADMIMBr) and 1-ethyl-3-
methylimidazolium acetate (EMIMAc)
20 1 M CED is solvent for the SCAN-method for determining the solution viscosity (an calculation of molecular weight).
Axial projection of cellulose I
(top) and cellulose II (bottom)

