Basic HTML Version
123
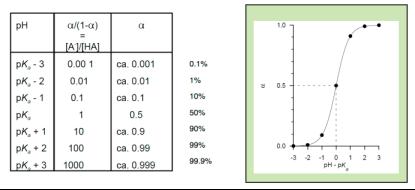
It follows from the Henderson-Hasselbach equation that it the polymer is 50%
dissociated, i.e.
α
= 0.5, then pH = pK
a
. In other words, when pH equals pK
a
then the polymer is 50% dissociated. Each molecule has 50% of its full
charge.
It also follows from the same equation that when pH is one unit below pK
a
,
then
α
= 0.1. The full picture follows from the table and figures below:
The table above (1% - 10% - 50% - 90% - 99% rule) is much used to quickly
estimate the charge profile in biopolymers, and can further be used to predict
the isoelectric point (pI) of peptides and proteins.
To accurately determine the degree of dissociation (
α
) the Henderson-
Hasselbach equation must be solved, leading to the following analytical
expression:
α
=
1
1
10
pH
−
pK
a
+
1
⎛
⎝⎜
⎞
⎠⎟
The formula is useful when making computer programs (or worksheets) to
simulate or analyze titration data.

