Basic HTML Version
114
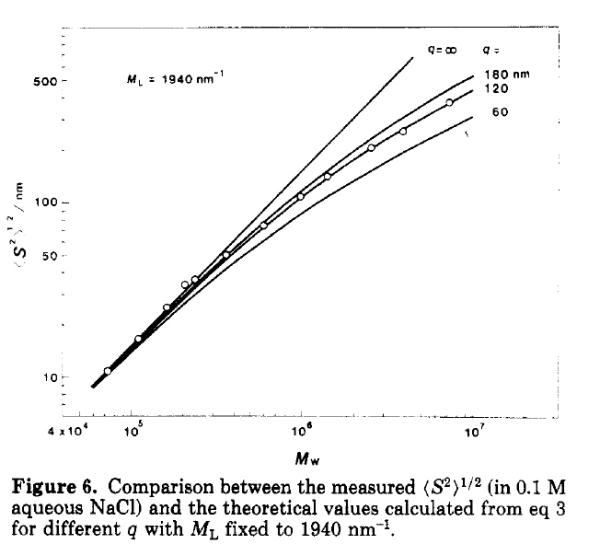
In this case M
L
was determined from the chemical composition combined with
X-ray crystallography data in the following way:
The repeating unit of xanthan is given in Section 1.7. By summation of all the
atoms (including the counterions) we find the repeating unit (fully pyruvated,
and partially acetylated in this case) has a mass of 970 g/mol (Da) (and 848 if
no pyruvate and acetate). Each glucose residue in the backbone is (from X-
ray) 0.5 nm, hence M
L
= 970/(2*0.5) = 970 nm
-1
. Since xanthan is double
stranded, M
L
becomes 1940 nm-
1
. This value is used in the figure above.
The same type of procedure can in principle be used for [
η
]-M data, but the
formulae are more complicated and not so convenient to process in a
spreadsheet, for example. However, it is much used because [
η
] data are
easily obtained over a larger interval of molecular weights than R
G
.
Again, take a look at the data in the table. The range of q-values goes from
less than 1 nm for the compact dextrans to 150 nm for triple-stranded
scleroglucan. Do the other values make sense from what you have learned
about these polymers?

