Basic HTML Version
107
2.2.10. How
small
chains
can we analyse using
the
random
coil model?
We have repeatedly stated the necessity of having sufficiently long chains for
the random coil model to be valid and applicable. How can we know if this is
the case? How short can the chains be before it is no longer ‘infinite’ and start
to approach the rod limit?
If data for M and R
G
have been obtained over a sufficiently wide range of
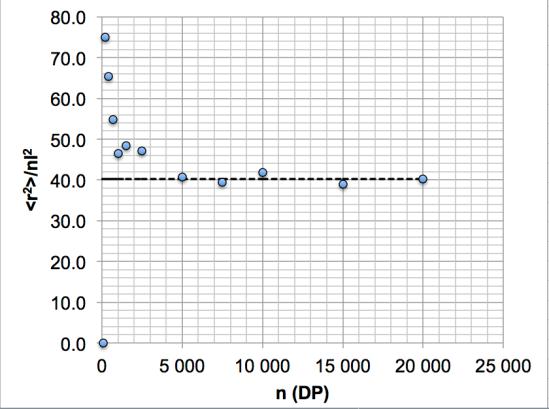
chain lengths one may observe deviations such as in the figure below:
Figure 48
The figure shows that a horizontal line is only obtained when DP (or n) is
larger than 5000, which is the effective lower limit below which ‘n <
∞
’ and the
formulae for random coils no longer apply.
In Section 2.3. another model will be introduced where such restrictions are
not present, and C
∞
can be determined (indirectly) on the basis of lower
molecular weights.
2.2.11. Other
stiffness parameters based on
the
random
coil
model.
We sometimes encounter other stiffness parameters, especially in older
literature, which also are based on the random coil model. In essence, they
contain the same information as C
∞
, and are actually related to C
∞
through
simple relationships.

